These Places Are Removing Surveillance Cameras – Privacy vs. Security
In recent years, the widespread use of surveillance cameras in public and private spaces has sparked significant debate worldwide. While cameras can play a crucial role in enhancing security, their presence has also raised serious concerns about privacy violations. Legal disputes over camera installations have emerged in various regions, with courts increasingly ruling in favor of privacy rights and ordering the removal of certain surveillance systems in hotels, restaurants, student dormitories, and public bathhouses.
This raises a critical question: If surveillance cameras are removed or restricted in certain areas, how can we strike a balance between ensuring security and protecting individual privacy?
What Products Can Replace Cameras?
Amid growing discussions around privacy and security, sensor technologies have gained increasing attention, with lidar being highlighted as one of the most promising alternatives.
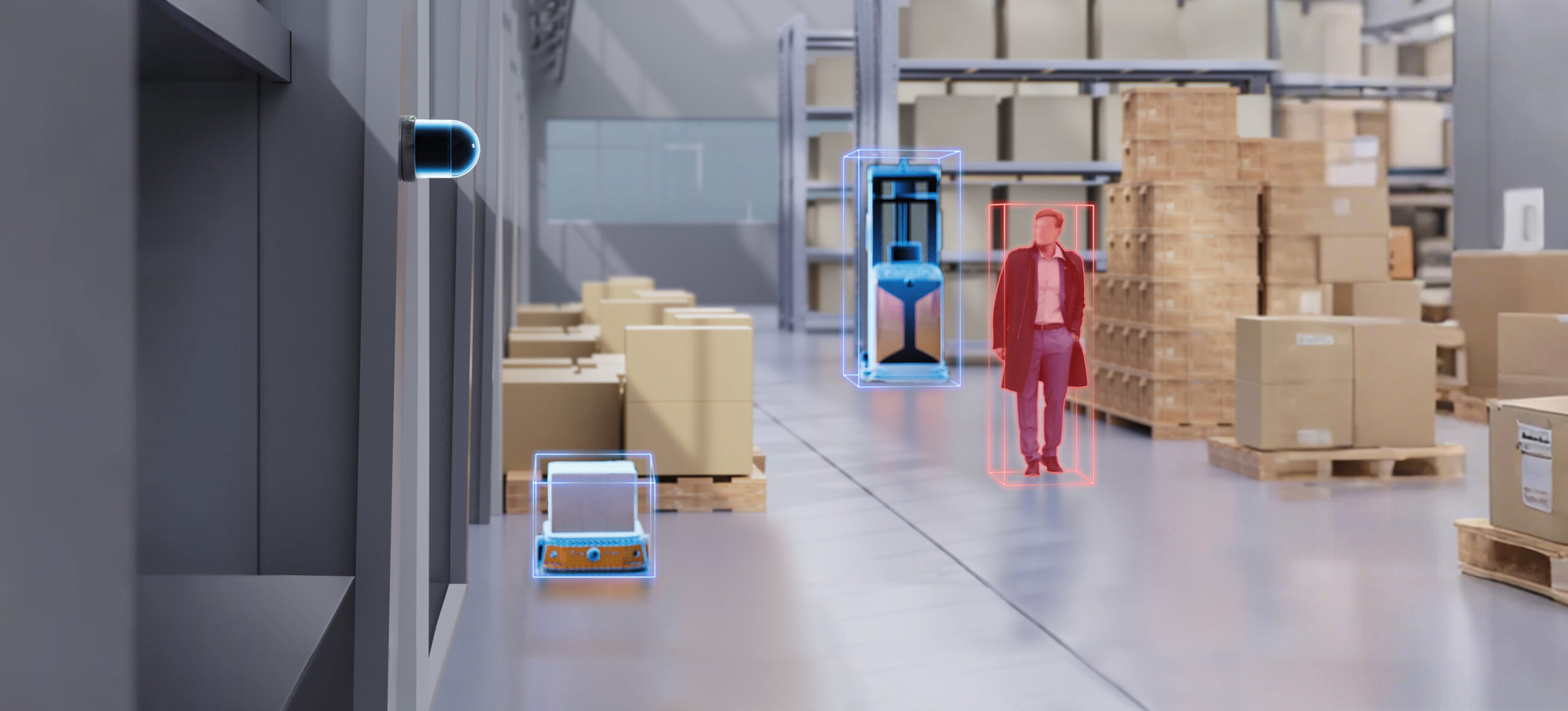
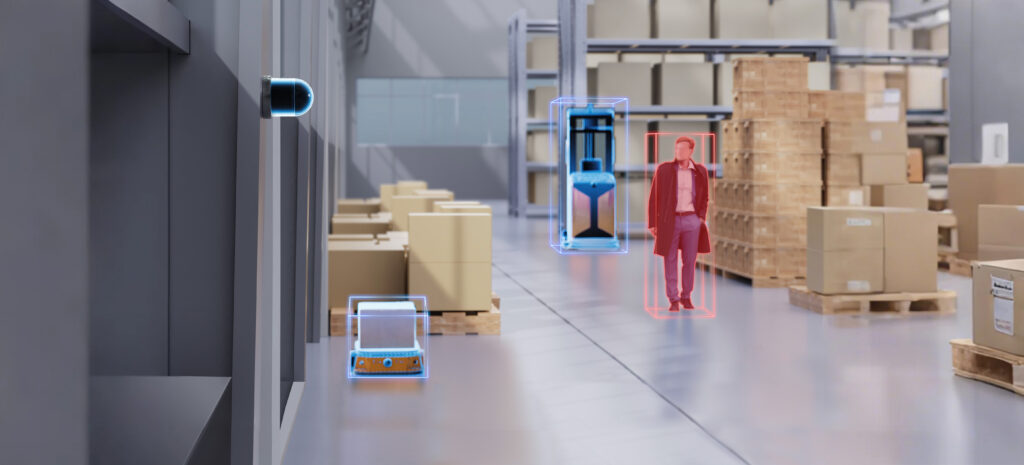
Lidar, like cameras, can offer real-time perception of both people and their surroundings, making it a strong contender in ensuring public safety without compromising privacy.
Why Lidar?
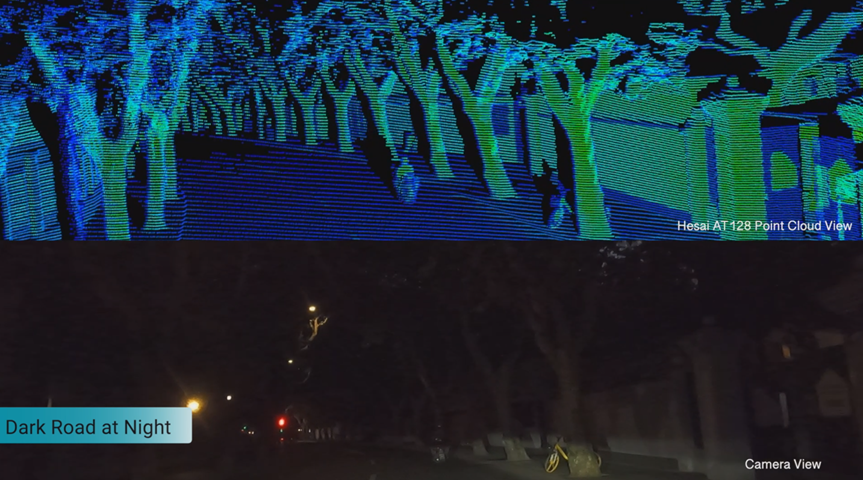
Lidar measures distances and constructs 3D environmental models by emitting laser beams, without relying on visible light. This allows it to function effectively even in complete darkness. In other words, Lidar can accurately detect pedestrians and objects even at night or in harsh weather conditions, significantly reducing false alarms in security systems.
A study by Parks Associates found that false alarms are the leading reason people remove cameras from their homes. Around 62% of security system users experienced false alarms in the past year, and in some countries, false alarms can incur fines of up to $250. With lidar, such incidents are minimized.

Unlike cameras, lidar does not capture personal information such as facial or other biometric data. Instead, it focuses on features like object shapes, positions, and the surrounding environment, which ensures security while respecting privacy. This makes lidar an ideal solution for those seeking to protect privacy while maintaining safety.

Industry experts point out that compared to other detection methods such as infrared, fiber optics, and video cameras, lidar offers distinct advantages, including a compact size, lightweight design, strong anti-interference capabilities, high reliability, and superior resolution. These features enable lidar to precisely detect intrusions and provide early warning alerts.
Moreover, lidar has a wide range of applications beyond security for sensitive areas. It is also widely used in smart traffic, autonomous driving, robotics, and more, demonstrating its cross-industry and multi-field value. As sectors like smart factories, smart homes, and industrial automation continue to expand, the demand for lidar is expected to grow steadily in the future.
Lidar’s Applications Across Industries
In recent years, lidar has seen increasing adoption in stationary applications. In addition to real-time perception of people and objects, lidar excels in privacy protection, adaptability in complex environments, and high-precision, making lidar a valuable complement to traditional security measures, particularly in privacy-conscious regions like Europe and North America.
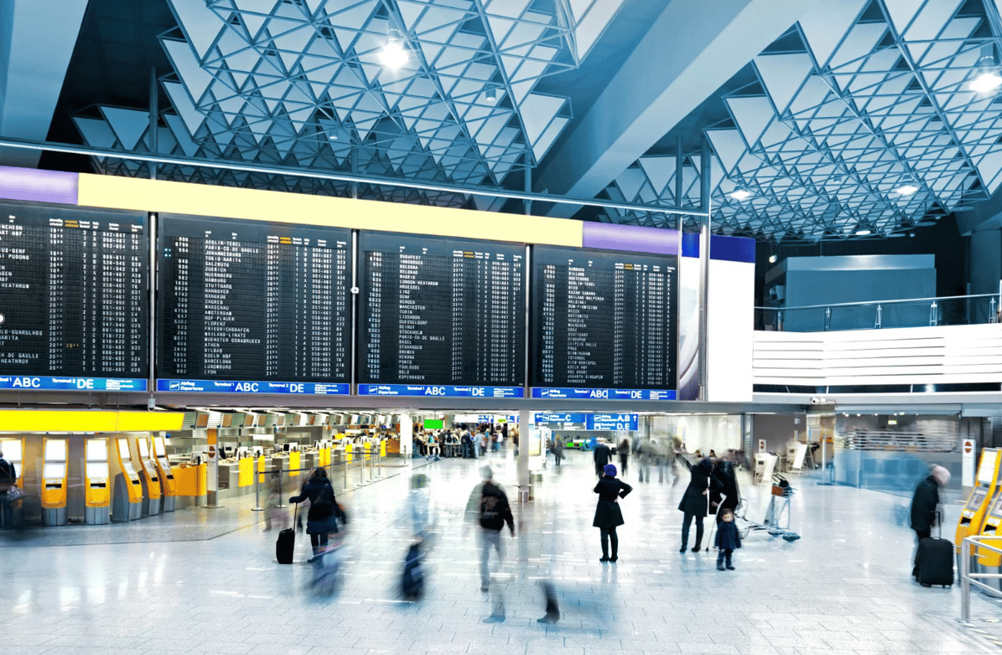
Beonic, a well-known AI software development company, has successfully applied lidar technology to airport traffic analysis for security solutions by partnering with Hesai. This collaboration provides airports with safe, efficient, and precise technical support for security management. The solution combines data from cameras, lidar, Wi-Fi, parking systems, and flight information systems to provide a comprehensive view of passengers’ journeys from parking to boarding. This enables intelligent airport operations in areas such as crowd management, gate scheduling and optimization, queue monitoring and alerts, and workforce optimization. Additionally, such customized solutions are highly applicable to other high-traffic locations, including transportation hubs, shopping malls, and stadiums.
Notably, while improving security management efficiency, lidar technology does not capture or store facial data. While maintaining security and providing operational insights, this ensures personal privacy remains fully protected.
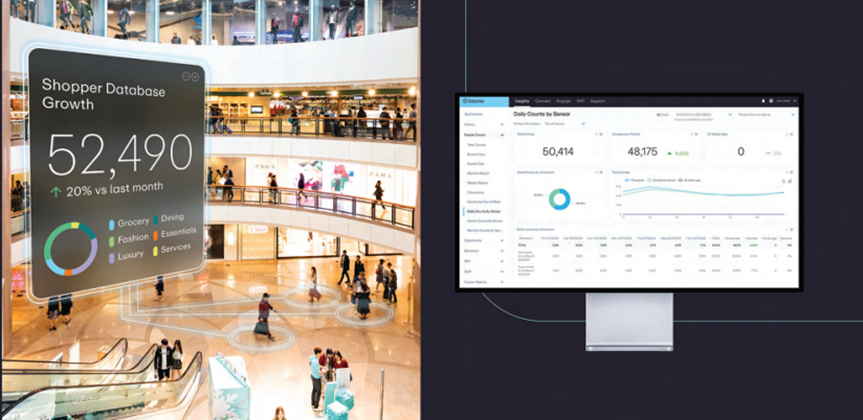
Furthermore, since lidar possesses excellent perception capabilities, it surpasses any other sensor in terms of accuracy and reliability for detecting objects and pedestrians. This advantage also extends to other stationary applications, such as smart factories.
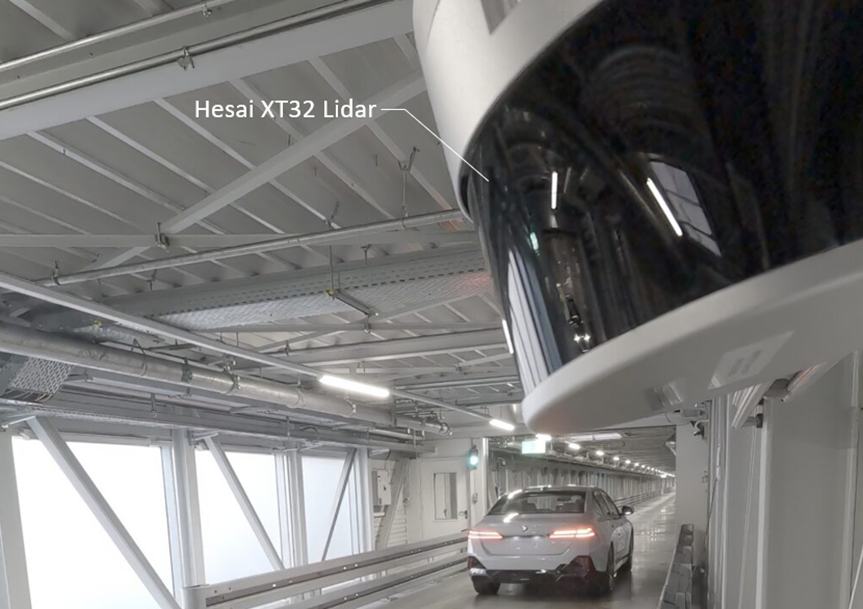
With the aid of Hesai’s 3D lidars, BMW’s smart factory in Germany has implemented an Autonomous Vehicle Management (AVM) system, enabling newly produced vehicles to be automatically dispatched from the production workshop to the final assembly processing area without human intervention. This eliminates the cumbersome process where workers would otherwise need to return to the production workshop after each vehicle is delivered to its destination.
BMW initially applied this AVM technology to its 5 Series and 7 Series models at the Dingolfing plant in Germany. It has since expanded the system to the MINI Countryman at the Leipzig plant and additional BMW models. The technology has now been successfully deployed across three of BMW’s smart factories in Europe and is set to be introduced to multiple BMW plants in Europe and North America in the future.

Driving Down Costs for Broader Adoption
It is widely recognized that cost is the ultimate factor determining whether a product can achieve large-scale adoption. In this regard, Hesai has significantly driven down the cost of lidar through technological advancements and large-scale production by developing core components in-house. Over the past eight years, Hesai has achieved a remarkable 99.5% reduction in lidar costs, bringing prices down from hundreds of thousands of dollars per unit to the launch of products priced in the hundred-dollar range. This breakthrough in cost efficiency has truly democratized high-performance 3D lidar, making it accessible for various industrial applications.
This cost reduction not only accelerates the rapid development of the lidar market but also unlocks new possibilities for applications across various specialized sectors.
For example, in the security inspection sector, lidar serves as the “eyes” of unmanned inspection robots. Take Hesai’s newly released JT series lidar as an example—JT features the world’s widest 360° × 187° ultra-hemispherical field of view in a compact design. It excels in close-range detection, effectively sensing objects even when they are in direct contact with the sensor, ensuring zero blind spots for close-range perception. Additionally, with Hesai’s proprietary waveform processing technology, JT can provide rain and fog alerts and filter out noise points, enabling reliable all-weather perception even in challenging conditions such as heavy rain, fog, or intense sunlight. This makes it highly adaptable to various demanding operational scenarios.

It is foreseeable that as demand for lidar continues to grow, the technology will play a significant role in applications such as intrusion detection, infrastructure maintenance, traffic management, as well as industrial robotics.
Conclusion
Lidar is not only the “airbag” of autonomous driving, but also the “guardian” of commercial and security sectors. While new regulations have imposed restrictions on camera installations in certain areas, this does not mean that security should be compromised. Instead, it calls for new alternative solutions. With continuous technological advancements and ongoing cost reductions, lidar is shaping the future of the stationary application industry. It is expected that sensor-based solutions, including lidar, will emerge as a superior alternative to cameras, ensuring both privacy protection and security.



